Omaha Platform: A Historical Perspective

Introduction
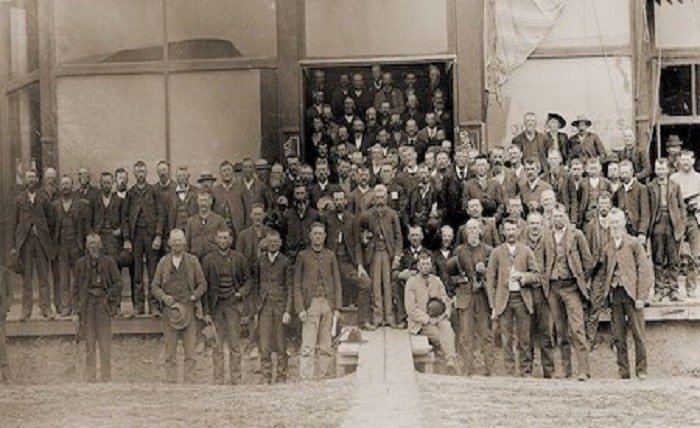
The Omaha Platform is a foundational document in the history of American populism. Adopted in 1892 by the Populist Party, it outlined the grievances of rural Americans and proposed radical reforms aimed at addressing economic inequality and political corruption. This comprehensive guide explores the origins, key elements, and enduring impact of the Omaha Platform.
The Origins of the Omaha Platform
The Omaha Platform was born out of the economic hardships faced by American farmers in the late 19th century. The formation of the Populist Party, also known as the People’s Party, was a response to the exploitation by big businesses and the failures of the existing political system to address their needs. Understanding the origins of the Omaha Platform provides insight into the social and economic context of the era.
Key Principles of the Omaha Platform
The Omaha Platform presented a clear set of demands aimed at reforming the economic and political landscape of the United States. Key principles included the direct election of senators, a progressive income tax, the nationalization of railroads, and the implementation of a flexible currency system. Each of these points addressed specific issues that were crucial to the Populist movement.
The Demand for Economic Reform
A significant aspect of the Omaha Platform was its focus on economic reform. The Populists advocated for the free coinage of silver to inflate the currency and make it easier for farmers to pay off debts. Additionally, they called for government control of railroads and telegraphs to reduce exploitation by monopolies. These economic demands were designed to alleviate the financial burdens on rural Americans.
Political Reforms Advocated by the Omaha Platform
The Omaha Platform also emphasized the need for political reforms. It proposed the direct election of U.S. senators, a measure aimed at reducing corruption and increasing accountability. Furthermore, the platform called for the implementation of the secret ballot to protect voters from intimidation and ensure fair elections.
Social Reforms and Labor Rights
Social reforms were another critical component of the Omaha Platform. The Populists supported the eight-hour workday and sought to improve labor conditions for industrial workers. They also advocated for the establishment of postal savings banks to provide safe and accessible banking options for ordinary Americans.
The Impact of the Omaha Platform on American Politics
The Omaha Platform had a profound impact on American politics. It galvanized the Populist movement and influenced subsequent political agendas. Many of the reforms proposed in the platform were later adopted in some form, demonstrating the lasting influence of the Populist Party’s vision for economic and political change.
The Legacy of the Omaha Platform
The legacy of the Omaha Platform extends beyond its immediate impact. It laid the groundwork for future progressive movements and reforms in the United States. The platform’s emphasis on economic justice, political transparency, and social equity continues to resonate with contemporary political discourse.
Challenges Faced by the Populist Movement
Despite its ambitious agenda, the Populist movement faced significant challenges. Internal divisions, external opposition from established political parties, and changing economic conditions all contributed to the decline of the Populist Party. Analyzing these challenges provides a comprehensive understanding of the movement’s rise and fall.
The Omaha Platform in Historical Context
Placing the Omaha Platform in historical context helps to appreciate its significance. It was a product of its time, reflecting the frustrations and aspirations of rural Americans during a period of economic transformation and political realignment. Understanding this context highlights the platform’s relevance to the broader narrative of American history.
Modern Relevance of the Omaha Platform
The principles and demands of the Omaha Platform continue to hold relevance in modern political discussions. Issues such as economic inequality, corporate influence in politics, and the need for democratic reforms are as pertinent today as they were in the 1890s. This section explores how the Omaha Platform’s legacy informs current political movements and debates.
Conclusion
The Omaha Platform remains a landmark in the history of American populism. Its bold vision for economic, political, and social reform addressed the pressing issues of its time and left a lasting impact on the nation’s political landscape. By understanding the origins, principles, and legacy of the Omaha Platform, we gain valuable insights into the enduring struggle for justice and equality in the United States.
FAQs
- What was the main goal of the Omaha Platform? The main goal of the Omaha Platform was to address economic inequality and political corruption by proposing comprehensive reforms such as the direct election of senators, a progressive income tax, and nationalization of key industries.
- Who adopted the Omaha Platform? The Omaha Platform was adopted by the Populist Party, also known as the People’s Party, during their national convention in Omaha, Nebraska, in 1892.
- What economic reforms did the Omaha Platform propose? The Omaha Platform proposed the free coinage of silver, government control of railroads and telegraphs, and a flexible currency system to alleviate financial burdens on farmers and reduce exploitation by monopolies.
- How did the Omaha Platform influence American politics? The Omaha Platform galvanized the Populist movement, influencing subsequent political agendas and leading to the adoption of many of its proposed reforms in later years.
- Is the Omaha Platform still relevant today? Yes, the principles and demands of the Omaha Platform remain relevant in modern political discussions, addressing issues such as economic inequality, corporate influence in politics, and the need for democratic reforms.